|
The wire rope core supports the strands laid
around it. The three types of wire rope cores arc
fiber, wire strand, and independent wire rope (fig.
13-3).
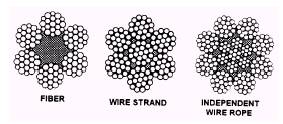
[Figure 13-3.-Core construction]
A fiber core may be a hard fiber, such as manila,
hemp, plastic, paper, or sisal. The fiber core offers
the advantage of increased flexibility. It also
serves as a cushion to reduce the effects of sudden
strain and acts as an oil reservoir to lubricate
the wire and strands (to reduce friction). Wire
rope with a fiber core is used when flexibility
of (he rope is important. . A wire strand core resists
more heat than a fiber core and also adds about
15 percent to the strength of the rope; however,
the wire strand core makes the wire rope less flexible
than a fiber core. . An independent wire rope core
is a separate wire rope over which the main strands
of the rope are laid. This core strengthens the
rope, provides support against crushing, and supplies
maximum resistance to heat.
|

|
6x7 Rope |
| Excellent abrasion resistance; less bending
fatigue resistance. Dragging and haulage in mines, inclined
planes and tramways, sand lines. |
| |
|

|
6 x 19 - Seale |
Characteristics
Resistant to abrasion and crushing : medium fatigue resistance
|
Typical Applications
Haulage rope, choker rope, rotary drilling line |
|

|
6x2l Filler Wire |
Characteristics
Less abrasion resistance more bending fatigue resistance |
Typical Applications
Pull Ropes, load lines, backhaul ropes, draglines |
|

|
6x25 Filler Wire |
Characteristics
Most flexible rope in classification: best balance of abrasion
and fatigue resistance |
Typical Applications
Most widely used of all wire ropes - cranes hoists, skip hoists,
haulage, mooring lines, conveyors, etc. |
|
|
6x26 Warrington Seale |
Characteristics
Good balance of abrasion and fatigue resistance |
Typical Applications
Boom hoists, logging and tubing lines |
|
